The Side Effects of Vitamin B-100

Your body needs the eight B vitamins for energy metabolism, red blood cell synthesis, cardiovascular health and proper growth and development. However, few Americans get as much as they need, says the Harvard School of Public Health. Manufacturers of vitamin B-100, a dietary supplement that contains at least 100 milligrams, 100 micrograms or 100 percent of the recommended dietary allowance of each B vitamin, claim their products can supply you with the nutrients you need for better health and more energy. The large amount of B vitamins in every dose may cause a variety of side effects. Speak to your doctor first.
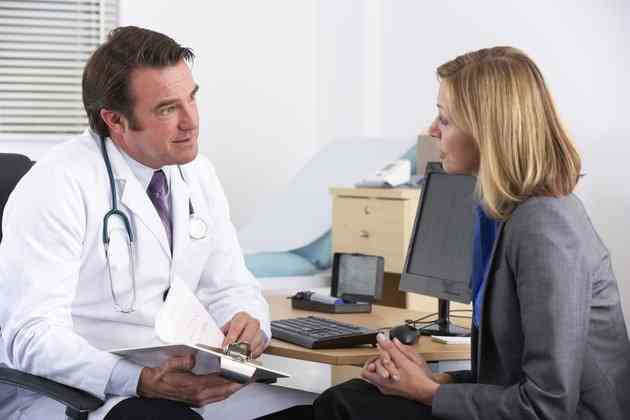
 Don't take vitamin B-100 until you've talked to your doctor. (Image: monkeybusinessimages/iStock/Getty Images)
Don't take vitamin B-100 until you've talked to your doctor. (Image: monkeybusinessimages/iStock/Getty Images)Side Effects of Niacin
A typical vitamin B-100 supplement contains 100 milligrams of niacin. That's far more than the 16 daily milligrams recommended for men and the 14 milligrams advised for women. Additionally, it exceeds the tolerable upper intake level, or UL, of 35 milligrams per day for adults set by the Institute of Medicine. Too much supplemental niacin can cause flushing, a condition characterized by red, tingling skin on your face, chest, arms and neck. It can also cause skin rashes and elevated blood glucose, and increase your risk of liver damage and ulcers.
Side Effects of Pantothenic Acid
Each 1-tablet serving of commercial vitamin B-100 supplies 100 milligrams of pantothenic acid, also known as vitamin B-5. Adults need only about 5 milligrams per day. No UL has been set for pantothenic acid, but the Institute of Medicine cautions against consuming more than is recommended. The high concentration in vitamin B-100 could cause diarrhea and thin your blood, leaving you more likely to bleed excessively when injured. Pantothenic acid interferes with the function of antibiotics like tetracycline and cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Side Effects of Thiamine
Men over 19 years old should have around 1.2 milligrams of vitamin B-1, or thiamine, each day; women should have 1.1 milligrams. Vitamin B-100 contains over 8,000 percent of this recommendation. While a UL hasn't yet been determined for thiamine, consuming an amount this high could cause an upset stomach. It may also interact with drugs such as digoxin, dilantin and diuretics like furosemide.
Side Effects of Riboflavin
The University of Maryland Medical Center says consuming more than 10 milligrams of riboflavin daily can increase your risk of suffering eye damage when exposed to the sun's ultraviolet rays. It may also result in itchy skin, discolored urine and a sensation of burning or numbness. You only need between 1.1 and 1.3 milligrams of riboflavin a day, though a vitamin B-100 complex tablet contains 100 milligrams. A UL for riboflavin hasn't been established.
Side Effects of Vitamin B-6
The 100 milligrams of vitamin B-6, or pyridoxine, supplied in each vitamin B-100 supplement equals the UL for the nutrient and is well over the 1.3 daily milligrams advised for a healthy adult. Taking this much in excess of the recommendation could cause a decrease in appetite, light sensitivity, nausea, stomach pain and skin problems. If your regular diet contains plenty of vitamin B-6 from foods like poultry, seafood, beans or whole grains, your intake might rise high enough to cause nerve damage in your legs.
Side Effects of Folic Acid
You need approximately 400 micrograms of folic acid daily to support the health of the nervous system and to aid in the production of DNA and RNA. Too much, however, and you could experience seizures, skin or digestive problems and insomnia. Vitamin B-100 contains 400 micrograms, or 100 percent of the RDA, per tablet. Taking the supplement along with a folic acid-rich diet could increase your risk of side effects. The UL of folic acid is set at 1,000 micrograms per day for adults.